Introduction
In today’s digital age, a reliable and fast internet connection has become a necessity for both personal and professional purposes. The ability to access information, communicate with others, and enjoy online entertainment largely depends on the type of internet connection you have. In this blog, we will explore various types of internet connections and discuss their speeds to help you make an informed choice.
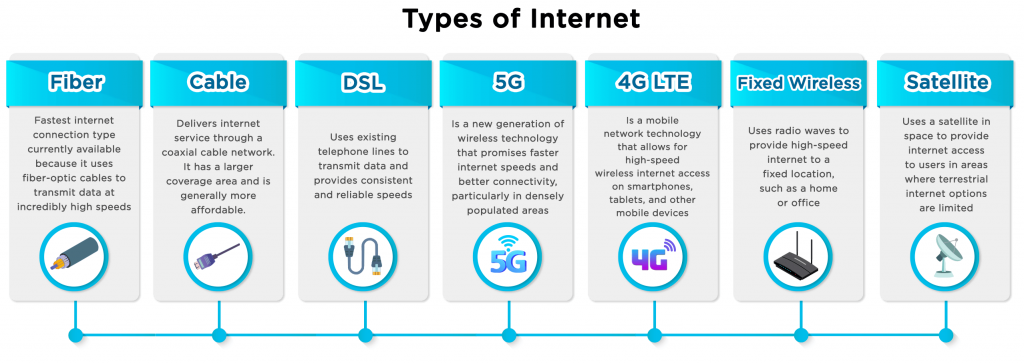
Types of Internet Connections and Their Speeds
- Dial-up Connection: Dial-up was one of the earliest forms of internet connections. It utilizes a standard telephone line to establish a connection. However, due to its limited bandwidth, dial-up offers a slow speed ranging from 56 kilobits per second (Kbps) to 128 Kbps. This type of connection is rarely used today, except in remote areas where other options are not available.
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line): DSL connections use the existing copper telephone lines for transmitting data. It offers faster speeds compared to dial-up, ranging from 128 Kbps to 100 Mbps (depending on the type of DSL). DSL speed largely depends on the distance between the user’s location and the nearest telephone exchange. As the distance increases, the speed decreases.
- Cable Internet: Cable connects users to the internet through the same coaxial cables that deliver cable TV signals. It provides higher speeds compared to dial-up and DSL, typically ranging from 10 Mbps to 1 Gbps. Cable speeds can vary depending on the number of users in your area, as the bandwidth is shared among multiple subscribers.
- Fiber Optic: Fiber optic is known for its exceptional speed and reliability. It uses thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as pulses of light. Fiber connections can offer speeds ranging from 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps (or even higher). The speed of fiber optic is not affected by distance, making it consistently fast regardless of the user’s location.
- Satellite Internet: Satellite is an option for those in remote or rural areas where wired connections are not available. It relies on satellites to transmit and receive data. Although satellite internet has improved over the years, it still tends to have higher latency and lower speeds compared to other options. The speeds generally range from 25 Mbps to 100 Mbps.
- Mobile Broadband: Mobile broadband allows users to access the internet wirelessly through cellular networks. The speed of mobile broadband can vary widely depending on the network technology (3G, 4G, or 5G), signal strength, and network congestion. While 4G LTE networks offer speeds ranging from 5 Mbps to 50 Mbps, 5G networks have the potential to deliver even faster speeds, reaching up to 10 Gbps.
Conclusion
Choosing the right internet connection is crucial to meet your specific needs for speed and reliability. While dial-up and DSL connections offer slower speeds, cable , fiber optic, and 5G mobile broadband provide significantly faster options. Satellite internet remains a viable choice for those in remote areas, despite its limitations. Understanding the types of internet connections and their associated speeds empowers you to make an informed decision based on your location and internet requirements.

