Introduction
In the interconnected world of the internet, the concept of net neutrality has emerged as a crucial aspect of ensuring an open and fair digital highway or landscape. Net neutrality, at its core, is the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally, without discrimination or preferential treatment by internet service providers (ISPs). As the internet plays an increasingly integral role in our daily lives, understanding and advocating for net neutrality becomes essential to safeguarding the democratic and innovative spirit of the online world.
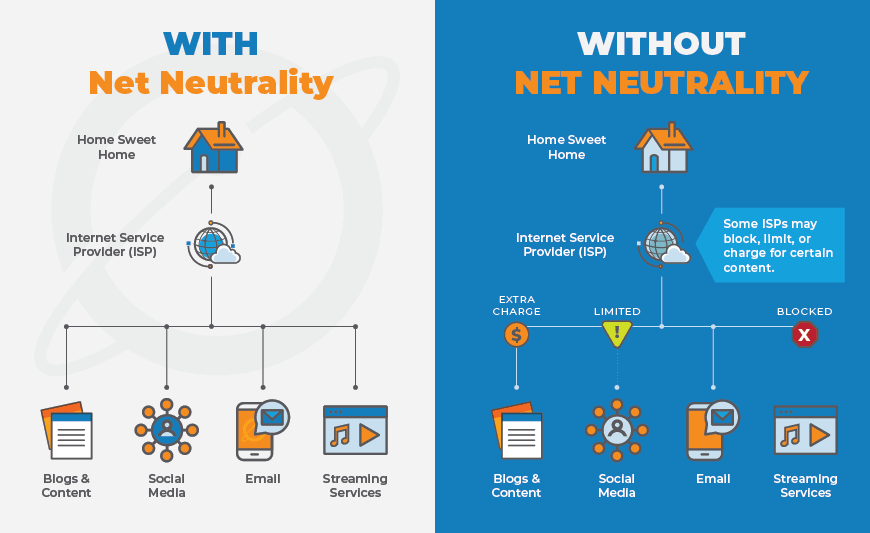
The Foundation of Net Neutrality
Net neutrality is founded on the principle that the internet should be an unbiased platform, treating all data equally regardless of its source, content, or destination. This means that ISPs should not be allowed to manipulate the speed, accessibility, or prioritization of internet traffic based on the websites or services being accessed.
Imagine the internet as a digital highway where data flows freely. Net neutrality ensures that every digital entity, be it a small blog or a multinational corporation, has an equal opportunity to reach users without facing discrimination. This principle promotes healthy competition, innovation, and the free exchange of ideas, contributing to a vibrant online ecosystem.
Challenges to Net Neutrality
Despite its fundamental importance, net neutrality has faced challenges and debates. Some ISPs argue that the ability to offer different levels of service and prioritize certain types of traffic could lead to improved user experiences, especially in scenarios where network congestion is an issue. However, critics argue that such practices could result in a tiered internet system, favoring established companies and stifling the growth of new, innovative startups.
In the absence of strong net neutrality protections, ISPs might be tempted to create “fast lanes” for certain content or services, effectively slowing down access to others. This potential discrimination raises concerns about the democratic nature of the internet, where every user, regardless of their resources, should have equal access to information and services.
Real-world Implications
The absence of net neutrality can have tangible consequences for both consumers and content providers. For instance, a scenario where ISPs can prioritize certain streaming services could lead to increased costs for consumers who may need to pay extra for faster access to their favorite content.
Furthermore, a lack of net neutrality could stifle innovation by creating barriers to entry for new players in the online space. Startups and smaller businesses may struggle to compete with established corporations that can afford to pay for preferential treatment from ISPs. This could result in a less dynamic and diverse digital landscape, ultimately harming consumers and limiting choices.
Global Perspectives on Net Neutrality
Various countries have approached net neutrality differently, with some implementing robust regulations to protect it, while others have taken a more hands-off approach. Advocates for net neutrality argue that clear and enforceable regulations are necessary to maintain a level playing field in the digital realm.
In the European Union, for example, net neutrality is protected under the Open Internet Regulation, which prohibits blocking or throttling of internet traffic and ensures that ISPs treat all data equally. In contrast, the situation in the United States has seen fluctuations, with net neutrality protections being repealed in 2017 and subsequently reinstated in some states.
Conclusion
Net neutrality is not just a technical concept; it’s a crucial component of a free and open internet. As we navigate the digital highway, it’s imperative to understand the implications of net neutrality on our online experiences, the democratic nature of the internet, and the potential for innovation and competition.
Advocating for net neutrality means supporting policies that ensure equal access for all, irrespective of the size or financial capabilities of online entities. It’s a call to preserve the internet as a democratic space where information, ideas, and services can flow freely, fostering a diverse and vibrant digital ecosystem that benefits everyone. As users, consumers, and digital citizens, we have a stake in the future of the internet, making the preservation and promotion of net neutrality a cause worth championing.

